29 Sep Open source microfluidics for spatio-temporal regulation of microenvironment for mammalian cell cultures
Abstract
“Microfluidic-based cell culture allows for precise spatio-temporal regulation of microenvironment, live cell imaging and better recapitulation of physiological conditions, while minimizing reagents’ consumption. Despite their usefulness, most microfluidic systems are designed with one specific application in mind and usually require specialized equipment and expertise for their operation. All these requirements prevent microfluidic-based cell culture to be widely adopted. Here, we designed and implemented a versatile and easy-to-use perfusion cell culture microfluidic platform for multiple applications (VersaLive) requiring only standard pipettes. Here, we showcase the multiple uses of VersaLive (e.g., time-lapse live cell imaging, immunostaining, cell recovery, cell lysis, plasmid transfection) in mammalian cell lines and primary cells. VersaLive could replace standard cell culture formats in several applications, thus decreasing costs and increasing reproducibility across laboratories. The layout, documentation and protocols are open-source and available online at https://versalive.tigem.it/.”

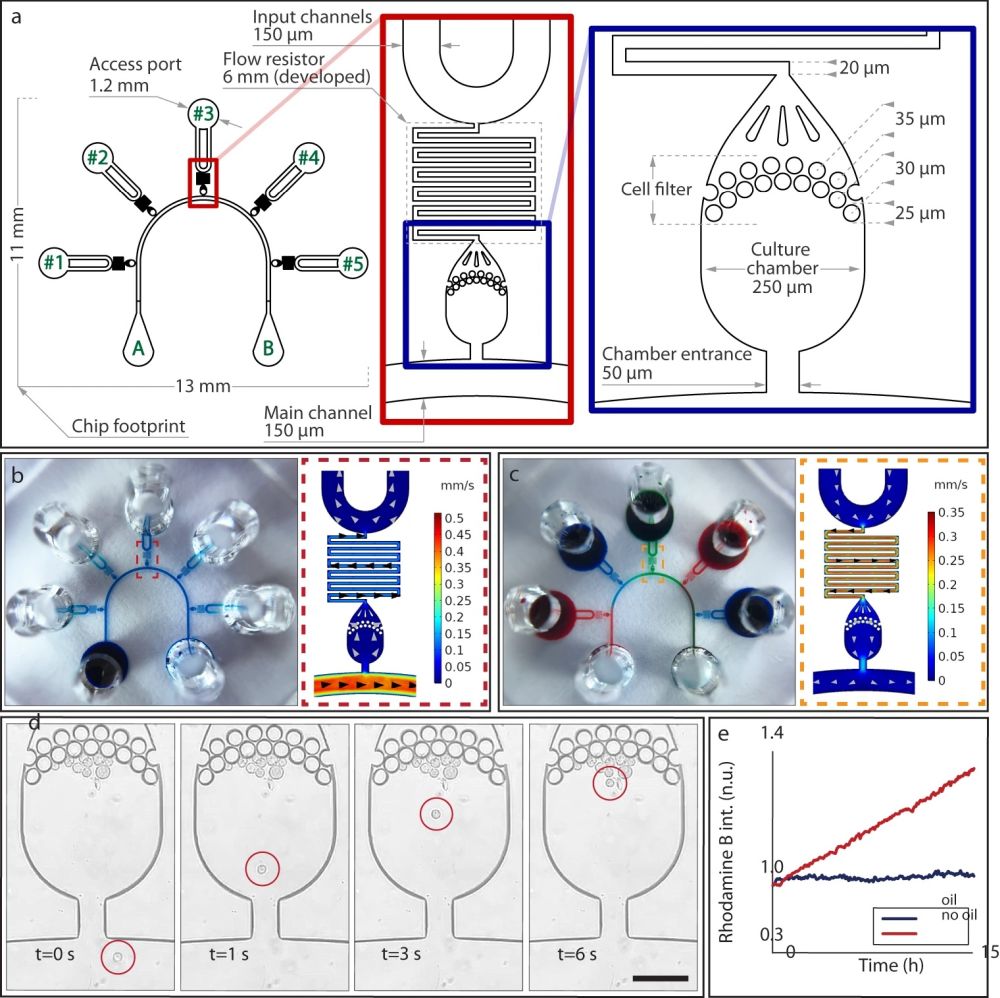
“a Layout of the microfluidics device with five independent chambers. On one side, all chambers are connected to the main channel that develops from port A to port B of the schematics. Fluids can be directed to each chamber independently by dedicated ports (ports #1 to #5 on the schematics). The serpentine flow resistor prevents shear stress to the cells during the device operations. b, c Modes of operation of VersaLive and their finite element simulations in COMSOL Multiphysics software (dashed inset). In the “perfusion” single-input mode (b), the main channel is exploited to deliver the same medium to all chambers at the same time. Multi-input mode (c) exploits the dedicated ports to deliver different inputs (i.e., media, chemicals) to each chamber avoiding cross-contaminations. d During cell loading, the cell suspension flows through the main channel and into the chambers. Once in the chamber, cells slow down and are eventually stopped by the filter features as predicted in the velocity profile of the simulation. Scale bar, 150 µm. e Solvent evaporation at the reservoirs was observed to increase the solute concentration of the channel content during perfusion. The effect was completely removed by the addition of a layer of mineral oil at the reservoirs. In the plot one single representative run is reported.” Reproduced under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License from Nocera, G.M., Viscido, G., Criscuolo, S. et al. The VersaLive platform enables microfluidic mammalian cell culture for versatile applications. Commun Biol 5, 1034 (2022).
Figures and the abstract are reproduced from Nocera, G.M., Viscido, G., Criscuolo, S. et al. The VersaLive platform enables microfluidic mammalian cell culture for versatile applications. Commun Biol 5, 1034 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-03976-8
Read the original article: The VersaLive platform enables microfluidic mammalian cell culture for versatile applications


