13 Aug On-demand wound disinfection with prodrugs generated using droplet microfluidics
Being one of the most promising areas of microfluidics, droplet microfluidics has been widely used for high-throughput data acquisition in the past decade. However, the potential of droplet microfluidic devices for generating products (therapeutics, cosmetics, etc.) with real-life applications has not yet been fully explored. For this week’s research highlight, we have selected a microfluidic advancement in which a droplet microfluidic chip was used to generate prodrugs encapsulated in hydrogel-based microspheres for bacterial inactivation and wound disinfection.
“The prodrug approach has emerged as a promising solution to combat bacterial resistance and enhance treatment efficacy against bacterial infections. Here, we report an adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-activated prodrug system for on-demand treatment of bacterial infection. “, the authors explained.

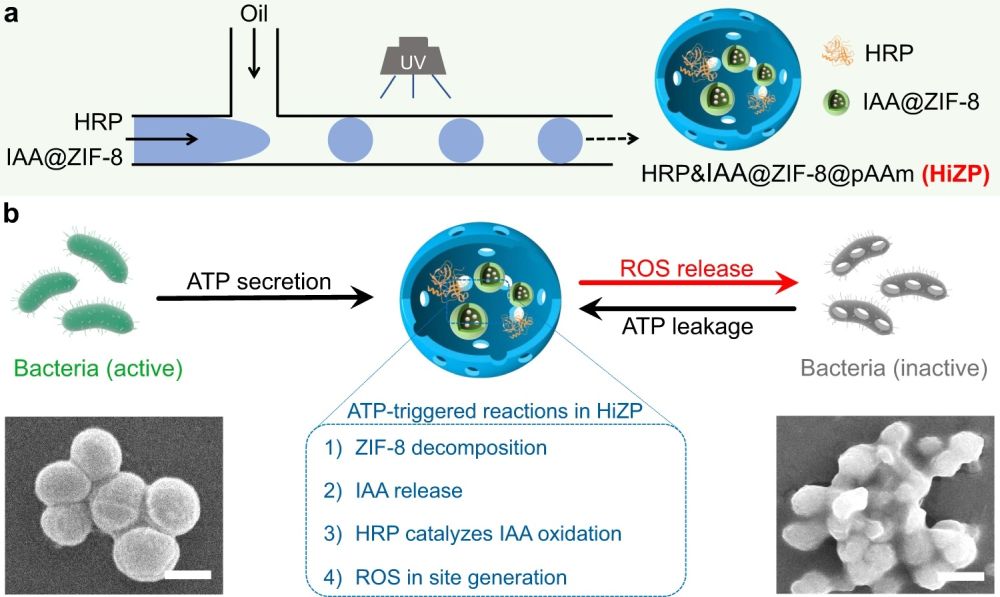
a The fabrication process of HiZP using droplet-based microfluidic technology. b ATP-triggered activation of HiZP for on-demand bacterial inactivation. Scale bars are 500 nm.” Reproduced under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License from Weng, Y., Chen, H., Chen, X. et al. Adenosine triphosphate-activated prodrug system for on-demand bacterial inactivation and wound disinfection. Nat Commun 13, 4712 (2022).
“From the in vivo antibacterial results, the applicability of HiZP was demonstrated for wound disinfection. Accordingly, our presented prodrug strategy not only provides a robust way to solve the contradiction of simultaneous transport and premature activation of the traditional HRP/IAA prodrug system but also offers an opportunity for utilizing ATP as a metabolic trigger to develop on-demand antibacterial agents.”, the authors explained.
Figures and the abstract are reproduced from Weng, Y., Chen, H., Chen, X. et al. Adenosine triphosphate-activated prodrug system for on-demand bacterial inactivation and wound disinfection. Nat Commun 13, 4712 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32453-3
Read the original article: Adenosine triphosphate-activated prodrug system for on-demand bacterial inactivation and wound disinfection


