05 Dec Cell mechanobiology made easier using microfluidic reconstruction of whole-cell stiffness maps
Abstract
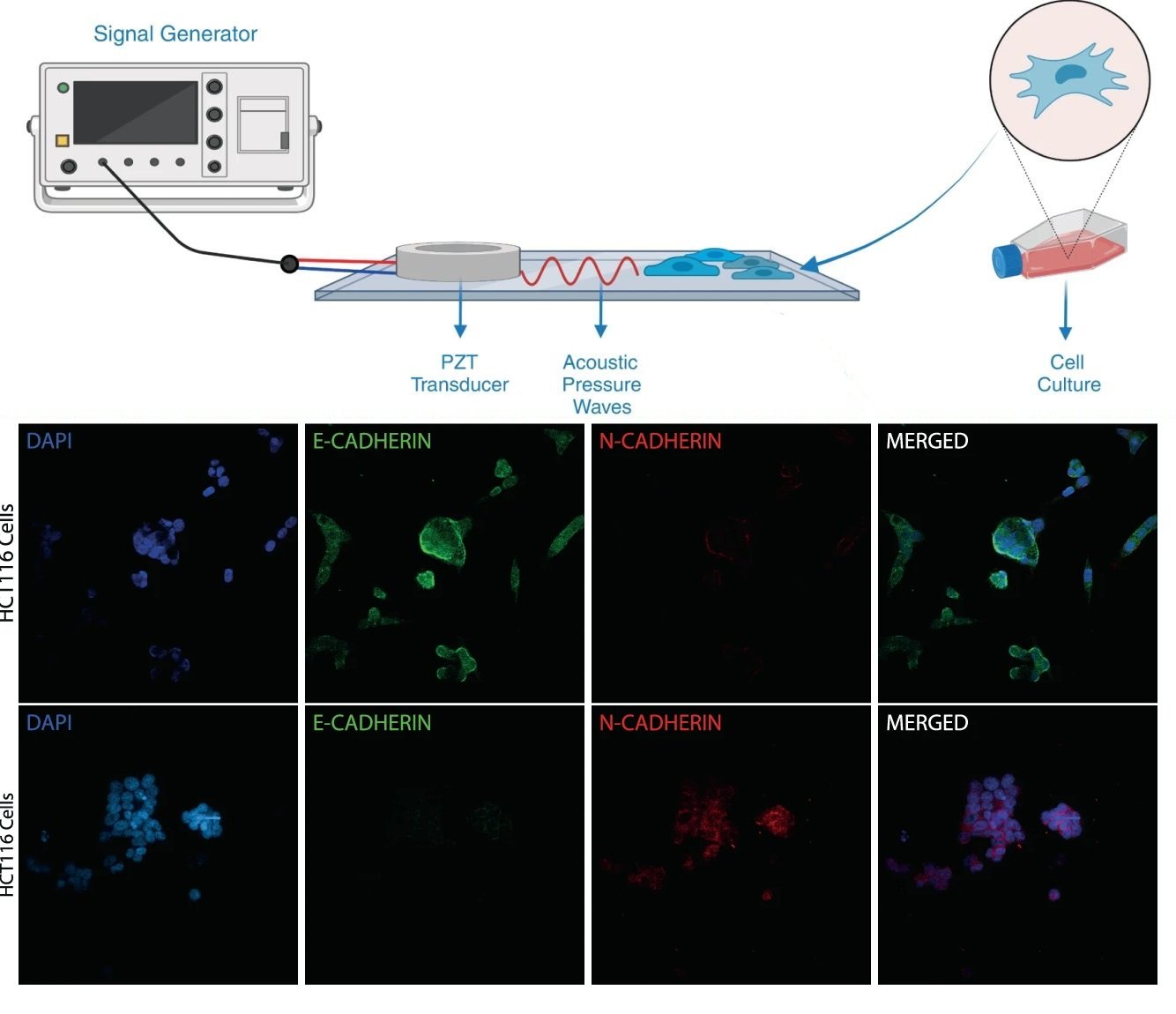
“Accurate assessment of cell stiffness distribution is essential due to the critical role of cell mechanobiology in regulation of vital cellular processes like proliferation, adhesion, migration, and motility. Stiffness provides critical information in understanding onset and progress of various diseases, including metastasis and differentiation of cancer. Atomic force microscopy and optical trapping set the gold standard in stiffness measurements. However, their widespread use has been hampered with long processing times, unreliable contact point determination, physical damage to cells, and unsuitability for multiple cell analysis. Here, we demonstrate a simple, fast, label-free, and high-resolution technique using acoustic stimulation and holographic imaging to reconstruct stiffness maps of single cells. We used this acousto-holographic method to determine stiffness maps of HCT116 and CTC-mimicking HCT116 cells and differentiate between them. Our system would enable widespread use of whole-cell stiffness measurements in clinical and research settings for cancer studies, disease modeling, drug testing, and diagnostics.”
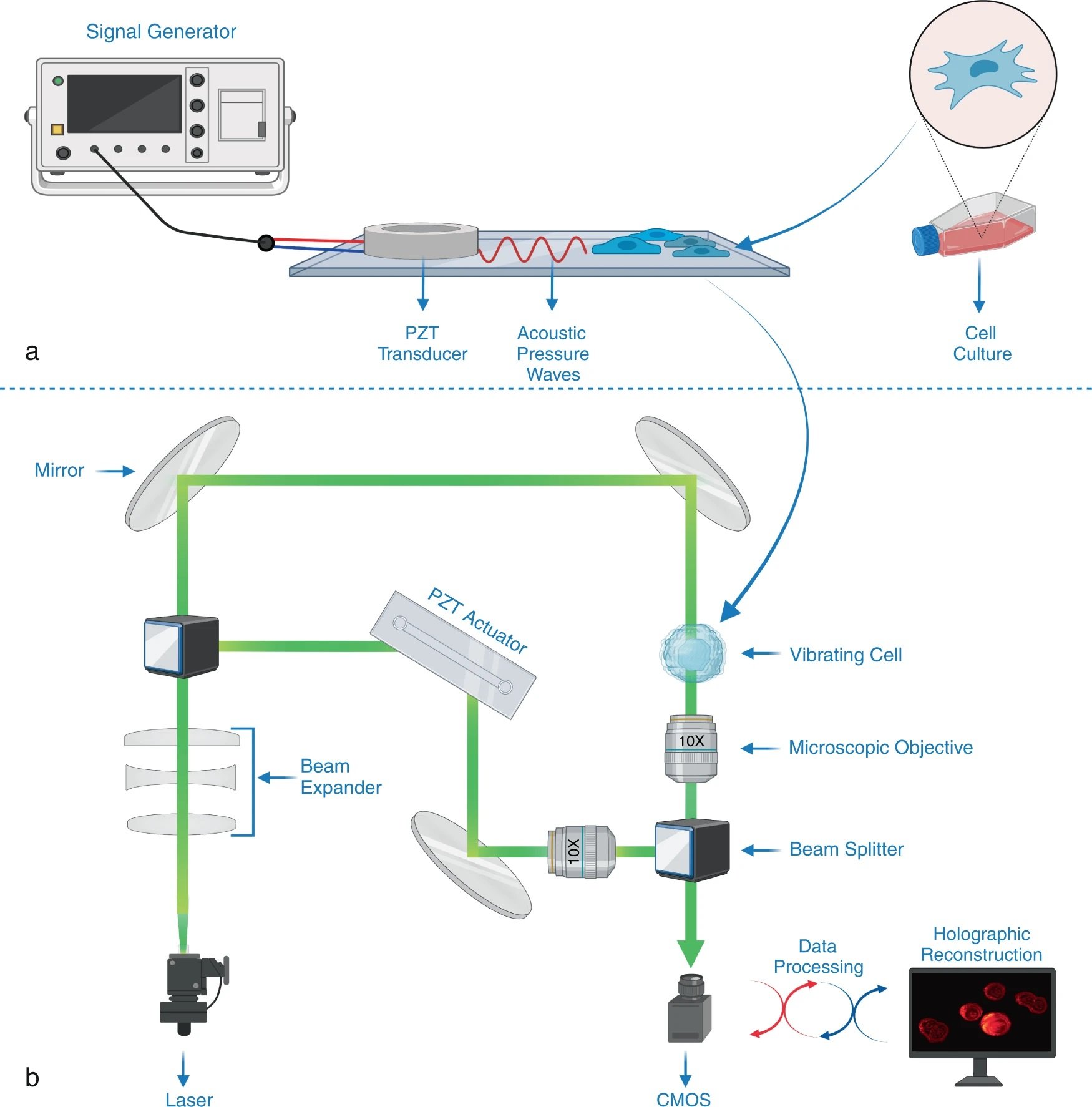
“a Compression and deformation induced on a cell with a low intensity bulk acoustic wave is measured by an interferometric imaging system to obtain whole-cell stiffness distribution. A PDMS fluidic chamber consisting of a PZT transducer, placed between a PDMS layer and a glass substrate it is bonded, is used to stimulate the cells in the chamber with high-frequency acoustic signals. b Holographic imaging system is composed of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer whose output port is monitored with a CMOS detector (see “Methods”). Light from a 527 nm He-Ne laser is divided into two by a beamsplitter (BS) and sent to two arms of the interferometer. The cell medium is placed in one of the arms, and the phase difference between the arms was varied using a high-frequency piezo actuator. Optical fields from both arms of the interferometer are recombined at a second BS, and one of the BS outputs is monitored with a high-speed CMOS camera that records the interference pattern. The acquired interferograms are processes to reconstruct stiffness maps (see “Methods” and Supplement for details. Created with BioRender.com.” Reproduced under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License from Varol, R., Karavelioglu, Z., Omeroglu, S. et al. Acousto-holographic reconstruction of whole-cell stiffness maps. Nat Commun 13, 7351 (2022).
Figures and the abstract are reproduced from Varol, R., Karavelioglu, Z., Omeroglu, S. et al. Acousto-holographic reconstruction of whole-cell stiffness maps. Nat Commun 13, 7351 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35075-x under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Read the original article: Acousto-holographic reconstruction of whole-cell stiffness maps


