01 Dec Dynamics of fluid-structure interaction at microscale revealed using microfluidics
Abstract
“A deformable microfluidic system and a fluidic dynamic model have been successfully coupled to understand the dynamic fluid–structure interaction in transient flow, designed to understand the dentine hypersensitivity caused by hydrodynamic theory. The Polydimethylsiloxane thin sidewalls of the microfluidic chip are deformed with air pressure ranging from 50 to 500 mbar to move the liquid meniscus in the central liquid channel. The experiments show that the meniscus sharply increased in the first 10th of second and the increase is nonlinearly proportional to the applied pressure. A theoretical model is developed based on the unsteady Bernoulli equation and can well predict the ending point of the liquid displacement as well as the dynamics process, regardless of the wall thickness. Moreover, an overshooting and oscillation phenomenon is observed by reducing the head loss coefficient by a few orders which could be the key to explain the dentine hypersensitivity caused by the liquid movement in the dentine tubules.”
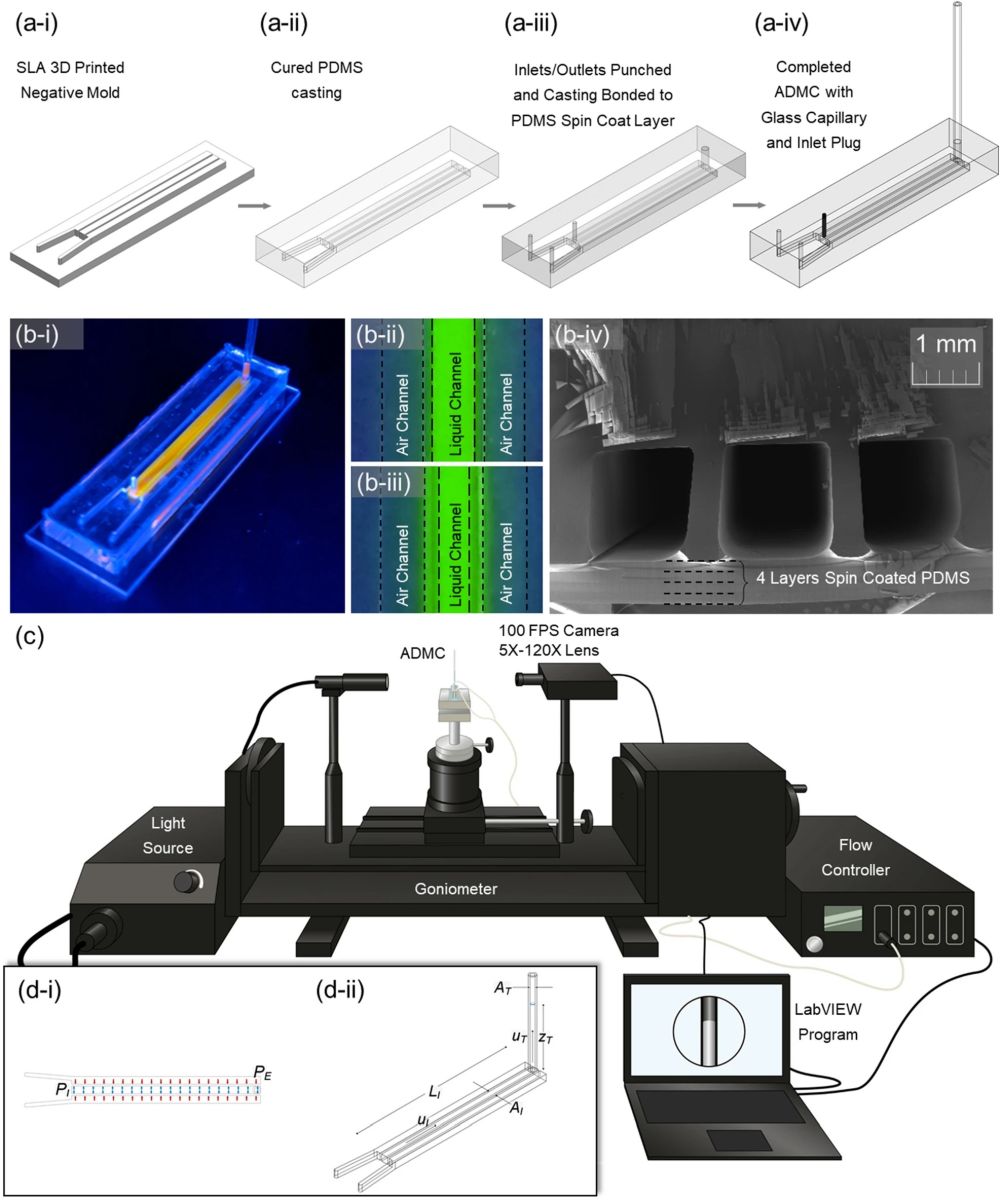
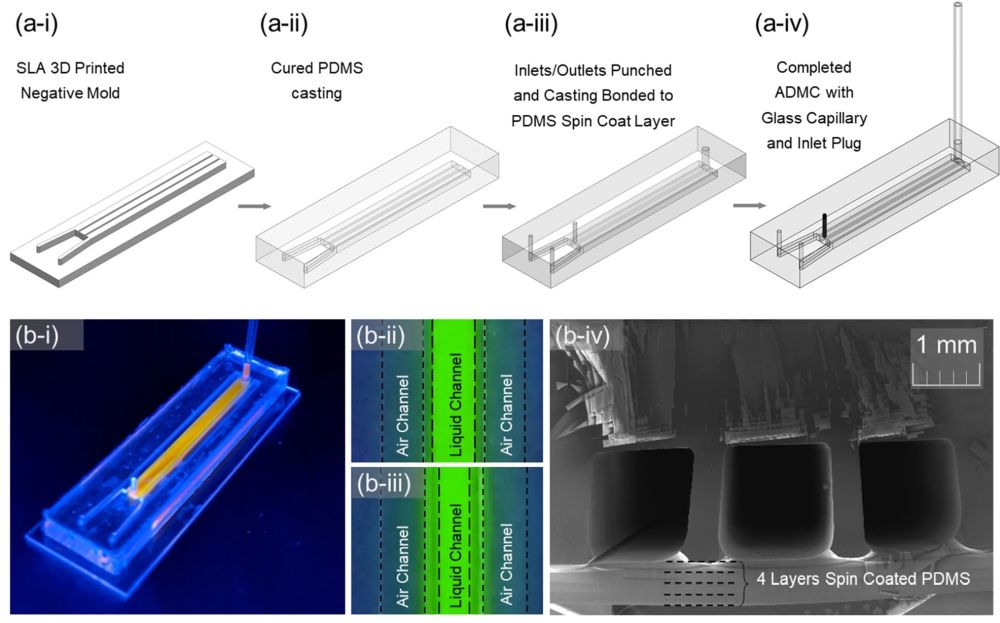
“(a) The fabrication process of the ADMC: (a-i) SLA 3-D printed negative mold. (a-ii) PDMS casting on the SLA mold. (a-iii) Inlets and outlet of the channels are punched. The chip is bonded with PDMS to a 1 mm thick spin coated PDMS layer. (a-iv) The central channel has a glass capillary inserted as a sight glass. After filling the central channel with distilled water, the inlet is plugged. (b-i) Photograph of the ADMC with orange fluorescent dye to distinguish between the liquid and air channels. (b-ii) and (b-iii) Before and after application of pressure to outside channels with green fluorescent dye. The thin wall between deflects and displaces fluid. (b-iv) Cross-section of the ADMC with a 500 µm sidewall. (c) The experimental setup—goniometer fitted with a 5X-120X magnification c-mount lens. The pressure is supplied using an ElvFlow controller. The camera and the flow controller are controlled using a LABVIEW program developed to collect images in synchrony with pressure sensor readings. (d) Schematics of the theoretical model. (Figure a(s) were drawn by SOLIDWORKS 2021: https://www.solidworks.com/media/solidworks-2021-pdm).” Reproduced under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License from Pas, C.t., Du, K., Pan, L. et al. Understanding the dynamics of fluid–structure interaction with an Air Deflected Microfluidic Chip (ADMC). Sci Rep 12, 20399 (2022).
Figures and the abstract are reproduced from Pas, C.t., Du, K., Pan, L. et al. Understanding the dynamics of fluid–structure interaction with an Air Deflected Microfluidic Chip (ADMC). Sci Rep 12, 20399 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-24112-w under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Read the original article: Understanding the dynamics of fluid–structure interaction with an Air Deflected Microfluidic Chip (ADMC)


