03 Sep Microporous hydrogels enhance the recovery of brain function in traumatic brain injury
Microfluidic devices have shown to have solutions for providing a means for controlled release and targeted delivery of drugs. For this week’s research highlight, we have selected one such microfluidic advancement. In this recent paper published in Nature Communications a droplet microfluidic chip was employed for generating injectable hydrogel microcapsules which could facilitate neuron survival and motor recovery as well as enhance mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor and improving angiogenesis.
“Here we present an adaptable conductive microporous hydrogel consisting of gold nanoyarn balls-coated injectable building blocks possessing interconnected pores to improve angiogenesis and recovery of brain function in traumatic brain injury. We show that following minimally invasive implantation, the adaptable hydrogel is able to fill defects with complex shapes and regulate the traumatic brain injury environment in a mouse model. “, the authors explained.

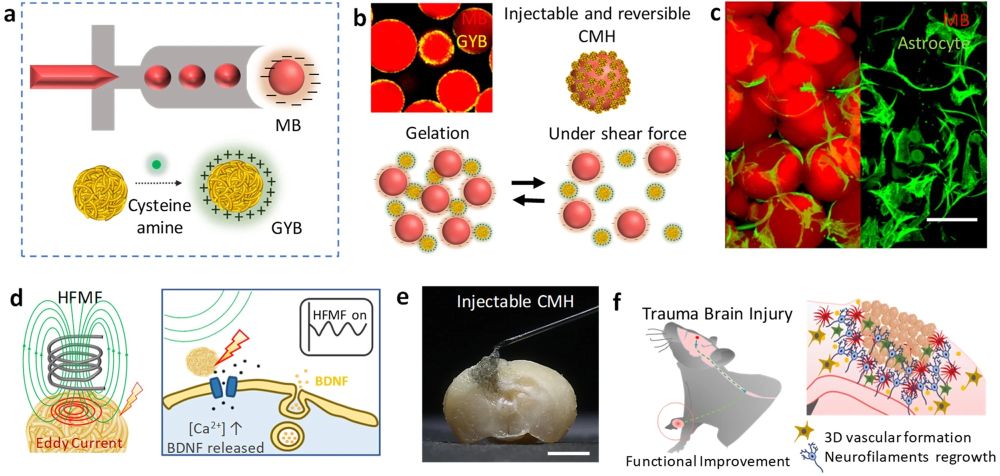
“a Schematic illustration of monodispersed gelatin methacrylamide (GelMA) injectable building blocks (microbeads, MBs) formation (upper); the process of synthesizing cys-GYB (lower). b Schematic illustration of injectable and reversible CMH. c Fluorescence image of a cell-laden micronetwork scaffold. Scale bar: 100 μm. d Schematic illustration of eddy current induced by HFMF (left) and promote BDNF releasing (right). e A photograph image represents the characteristic of injectable CMH into irregular cavity. Scale bar: 1.5 mm. f Schematic illustration of CMH with an electrical stimulation and axonal neurofiliments regrow in vivo.” Reproduced under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License from Hsu, RS., Li, SJ., Fang, JH. et al. Wireless charging-mediated angiogenesis and nerve repair by adaptable microporous hydrogels from conductive building blocks. Nat Commun 13, 5172 (2022).
” Integrating these functions, the hydrogel promotes an ∼2.5-fold and 3.15-fold increase in both peri-trauma vascularization and neuron survival in the trauma cavity, facilitating a restoration of brain functional connectivity (FC) in the corticostriatal and corticolimbic circuits. These conductive microporous hydrogels, which are characterized by tunable porosity and noninvasive brain stimulation via a temporally high-frequency magnetic field, create possibilities for hydrogel-mediated nerve therapy and potential use in clinics.“, the authors explained.
The figures and the abstract are Hsu, RS., Li, SJ., Fang, JH. et al. Wireless charging-mediated angiogenesis and nerve repair by adaptable microporous hydrogels from conductive building blocks. Nat Commun 13, 5172 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32912-x
Read the original article: Wireless charging-mediated angiogenesis and nerve repair by adaptable microporous hydrogels from conductive building blocks


